How to Control and Prevent Diabetes
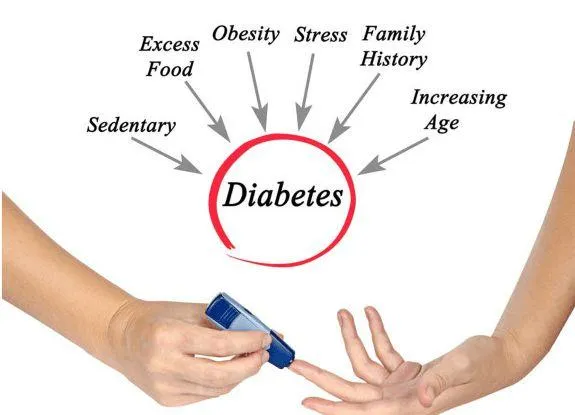
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide, particularly those over the age of 40. While genetics and age play a role in its development, lifestyle choices are significant factors in both controlling and preventing diabetes. Here are some practical steps to help manage and reduce the risk of diabetes:
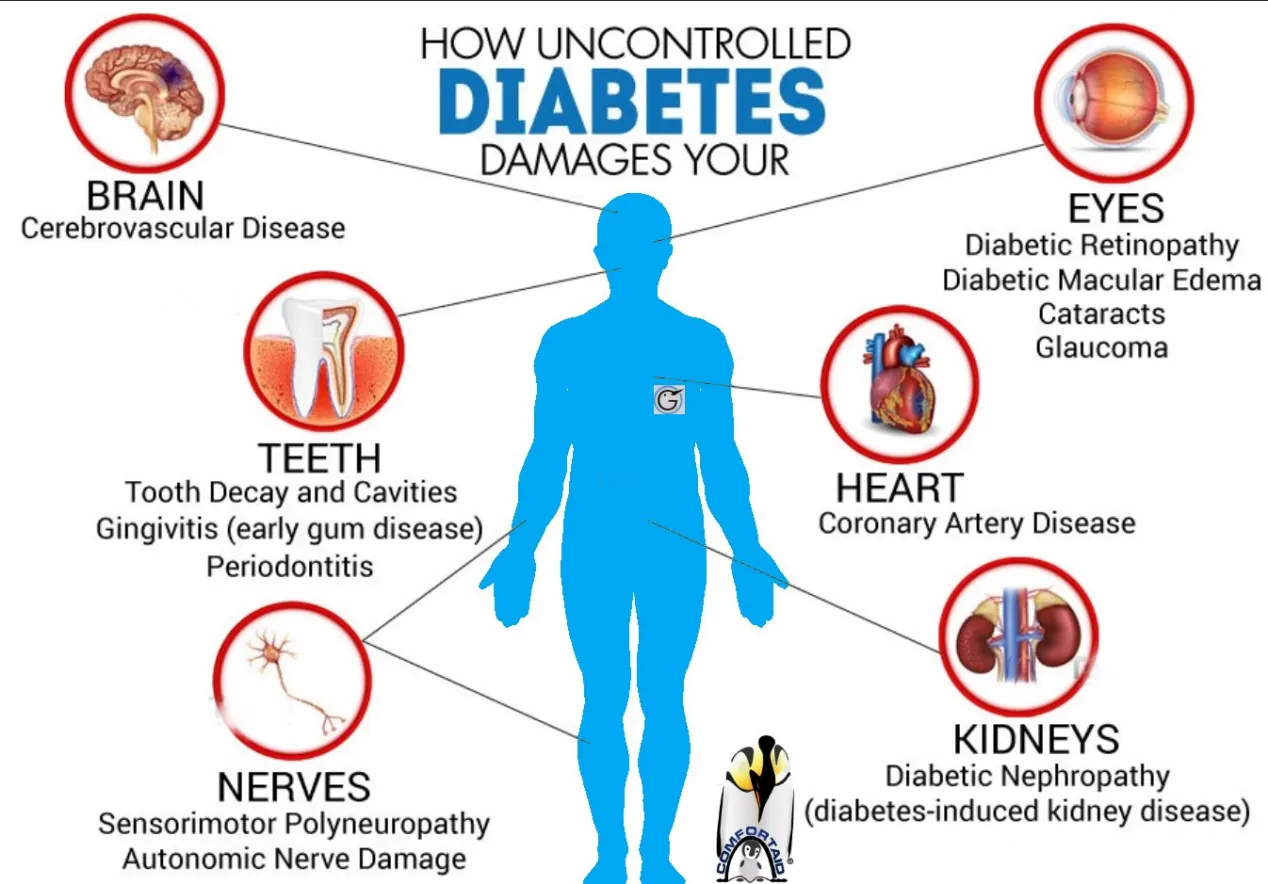
1. Maintain a Healthy Diet
A balanced diet is crucial for preventing and managing diabetes. Focus on the following:
Choose Whole Foods: Opt for whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Limit Sugar and Refined Carbs: Avoid sugary drinks, sweets, and processed foods that can spike blood sugar levels.
Control Portion Sizes: Overeating, even healthy foods, can lead to weight gain and insulin resistance.
Increase Fiber Intake: Foods like beans, lentils, and vegetables help regulate blood sugar levels.
2. Exercise Regularly
Physical activity is one of the most effective ways to prevent and control diabetes. Aim for:
Moderate Exercise: Activities like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling for at least 30 minutes a day, five days a week.
Strength Training: Incorporate resistance exercises twice a week to improve insulin sensitivity.
Stay Active Throughout the Day: Avoid prolonged sitting; take short walks or stretch regularly.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight, especially around the abdomen, is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. To achieve and maintain a healthy weight:
Set realistic weight loss goals (e.g., losing 5-10% of body weight).
Combine a healthy diet with regular exercise.
Monitor your progress and adjust your plan as needed.
4. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
Regular monitoring can help you understand how your body responds to food, exercise, and medication. If you’re at risk for diabetes:
Get regular check-ups with your doctor.
Use a blood glucose meter if recommended.
Keep track of your levels and share the data with your healthcare provider.
5. Manage Stress
Chronic stress can raise blood sugar levels and contribute to unhealthy habits. To manage stress:
Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
Prioritize sleep (aim for 7-9 hours per night).
Engage in hobbies or activities that bring joy and relaxation.
6. Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol
Smoking: Increases the risk of diabetes and complicates its management. Seek help to quit if needed.
Alcohol: Drink in moderation, as excessive alcohol can lead to weight gain and blood sugar fluctuations.
7. Regular Health Check-ups
Early detection is key to preventing diabetes-related complications. Schedule regular visits with your doctor to:
Check blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels.
Discuss any symptoms or concerns.
Update your prevention or management plan.
8. Educate Yourself
Stay informed about diabetes and its risk factors. Knowledge empowers you to make better choices and take control of your health.
Conclusion
While diabetes is a serious condition, it is largely preventable and manageable through lifestyle changes. By adopting a healthy diet, staying active, maintaining a healthy weight, and monitoring your health, you can significantly reduce your risk or better manage the condition if you already have it. Remember, small, consistent steps can lead to long-term health benefits. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice and support.
Take charge of your health today—your future self will thank you!
Featured Articles
 The best treatment for diabetesNo Longer a Dream! Diabetes Can Be 'Reversed'—Chronic Diseases May Reduce or Eliminate Medications (Exclusive Secrets Revealed)
The best treatment for diabetesNo Longer a Dream! Diabetes Can Be 'Reversed'—Chronic Diseases May Reduce or Eliminate Medications (Exclusive Secrets Revealed) Unlock Your Potential: Top Nutrition Courses, Life-Changing Benefits, and High-Paying CareersIn a world where health is a priority, understanding nutrition is your gateway to personal well-being and a lucrative career. Whether you’re looking to make healthier choices or become a sought-after professional, nutrition courses can help you achieve your goals.
Unlock Your Potential: Top Nutrition Courses, Life-Changing Benefits, and High-Paying CareersIn a world where health is a priority, understanding nutrition is your gateway to personal well-being and a lucrative career. Whether you’re looking to make healthier choices or become a sought-after professional, nutrition courses can help you achieve your goals. What Diet Should Kidney Disease Patients Eat??Managing kidney disease involves making informed dietary choices that can help slow the progression of the disease and maintain overall health. A well-balanced diet can alleviate symptoms and reduce the workload on the kidneys. This article will provide comprehensive dietary recommendations for individuals with kidney disease, focusing on foods that are beneficial while highlighting those to avoid.
What Diet Should Kidney Disease Patients Eat??Managing kidney disease involves making informed dietary choices that can help slow the progression of the disease and maintain overall health. A well-balanced diet can alleviate symptoms and reduce the workload on the kidneys. This article will provide comprehensive dietary recommendations for individuals with kidney disease, focusing on foods that are beneficial while highlighting those to avoid.